Meta Description: Learn the basics of measures of width, length, height, and depth, for example . Study right method and technique of calculation, practical use of measurements and measurements in a professional manner.
The world we live in is three-dimensional and dimensions play a central role in it, both in architectural plans as well as in packaging of products, which is a fundamental aspect of geometry . People in different sectors whose professions involve building, production, design, and logistics need to comprehend width, length, height, and depth. These four basic measurements give the spatial context through which places and position describe objects, as well as rectifications of our human physical environment.
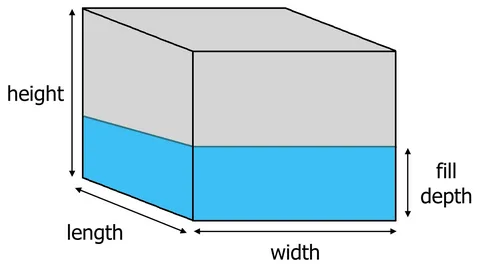
Dimensional concepts are important when you have to lay out a room to get furniture sizes, estimate costs of shipping packages or drawing a complex architectural building, as mathematics makes a person accurate, efficient, and competent in his/her profession. There are thorough descriptions of each dimension and other dimensions , with workable solutions and professional methods of precise measurement and usage.
Understanding the Four Primary Dimensions
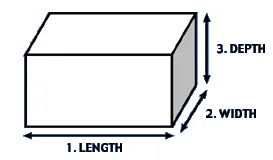
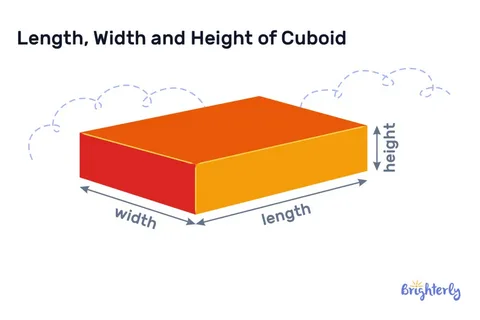
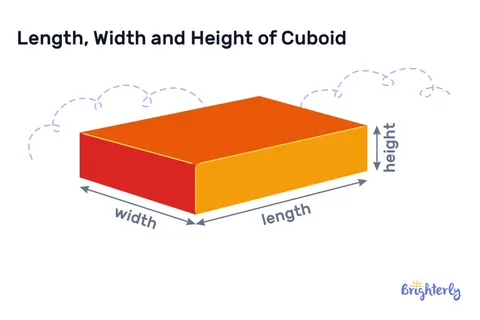
Length: The Foundation of Linear Measurement, often regarded as the longest dimension.
Length is the longest horizontal measurement of an object and is usually taken to be the distance between the extremes of an object along its main axis, the longer side . Length is the measuring scale baseline that is used in most settings to generate other dimensions. This rectangle dimension is basic in sustaining scales and is the reference of determining the area, volume and relationship of space.
Using the length measurement accurately is vital in professional industries in which it is used in different applications. Length is a determinant in construction which dictates the level of materials needed, and what is envisaged as the scope of the project as well as its structure spacing between two points. Designs based on manufacturing need exact precision when it comes to length requirements to verify compatibility of the components and accuracy during assembly. In retailing or e-commerce too, length is the important parameter in product description, delivery as well as customer fulfillment, alongside the consideration of width height and two dimensions.
Length matter has more than just a measurement. It affects the design aesthetics, functionality and user experience. The designers of furniture pay thorough attention to length just to make sure that the object will find its proper place to be located inside the space in three dimensions and provide a good visual effect. Length calculations can assist the engineer to calculate the load distribution, the point of stress, and even the structure that is required to be constructed on materials.
Width: The Horizontal Perpendicular Dimension and thickness.
Width is the dimension that is measured perpendicular to the length and it is the measure of the two sides of an object. This width, particularly at the corner, is a very important measure of stability, balance and space needs. Width has a direct impact on the footprint of an object and its dimension on fitting into assigned spaces or even between objects too.
The size of rooms in the buildings depends on the width measurements, height width specification the particularity of doors and the available spaces to locate pieces of furniture in the architectural setting. More extensive designs are also generally characterized by more stability that needs large spaces and substantial materials, especially at the edge of the structure . The width dimension is also part of the accessibility which means that building codes also stipulate minimum width specifications be met when it comes to areas like hallways or the doorways and emergency exits so that everyone could safely get past.
Width requirements are utilized by the manufacturing industries to enable compatibility among the products and efficient packaging. Shipping firms use measurements of width to decide the position of how containers are used and compute volumetric weight to reduce shipping costs. In retail experiences, shelf-sizes can be measured in terms of width and optimized to make the product display as well as the width height product as accessible as possible by providing a good viewing experience to the customer.
Height: The Vertical Dimension representing the vertical aspect of objects.
Height, which is derived from length that is vertical and represents the vertical extent from the base to the highest part of an object. This aspect is also critical when it comes to spatial planning, being compatible with the surroundings as well as satisfying the user needs. The visibility, accessibility, aesthetics and functionality ability of a broad range of applications are predetermined by height.
Height considerations in architectural projects is also very essential to adhere to building codes, zoning laws as well as safety standards. Height has been measured to create a balance in spaces, which is derived from ensuring good distribution of natural light as well as provision of space among the occupants. Vertical dimension also impacts on heating and cooling performance, where tall ceilings need to be thought of in varied ways than normal-sized spaces when it comes to HVAC.
Height is important in the designing of products, it defines storage needs, shipping limitations and the difference of possibilities of user interaction. Products that are tall might need particular packaging, handlings equipment and stores. On the other hand, products, which are of little height, can be beneficial to a small place, but may be compromised in functionality or esthetics.
Depth, which can be understood as a rectangle: The Third Horizontal Dimension.
Depth, which can be synonymous with breadth and dimension of width depending on view, can be described as the height or distance between the front and back of a given object. The dimension is vital in the determination of the extent to which a given object takes along its deep width, measured from one side, which is in line neither with the length nor the height. Necessity of depth measurements pertain to spatial planning, storage streamlining and suitability of functions.
In furniture design, depth can indicate how much pieces have been pushed into a room and will influence the traffic patterns as well as space comfort. Appliance such as kitchen appliances also have depth requirements to ensure they are standing correctly within countertops and cabinets. The depth specifications affect the level of comfort of the user, as well, and the seating should have a suitable depth so that the person sits correctly and relaxes.
Depth measurements are an essential feature of storage and logistic industries that are used to optimize warehouse structures, pack containers, and control the inventory. There will be effective use of space and a reduction of damages during handling and transport through an understanding of depth. In terms of length, retailing spaces rely on the depth measure to maximise the product display and optimise the availability of the products to customers. For instance, the distance optimization is that adequate depth ensures better visibility.
Dimensional Notation and Standard Conventions three dimensions
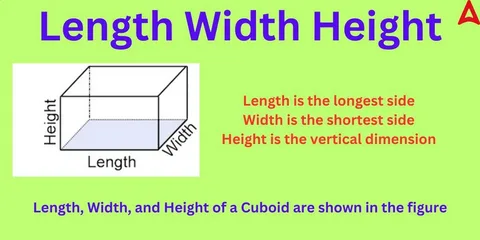
Industry-Standard Measurement Orders
Conventions that are followed by professional industries are standardized to present dimensional data in a precise way so that there is no need to communicate and they can avoid being involved in expensive mistakes. The most universal is the way it was described: Length, Width, and Height (L x W x H), which represent the third dimension .
In the packaging and shipping fields, it is common to see the word length notation Width x Depth x Height (W x D x H), with width (along the side-to-side) dimension, depth (along the front-to-back) dimension, and height (as measured by lifting the dimension up or down) dimension. This standard is based on type of packaging orientations and shipping container designs.
Length of the longest horizontal measure is commonly followed by Width or the shorter dimension and the Height or rise. In structures such notation is also commonly used, where Length, Width, and Height are used to describe the components of a structure. This standardization will involve ensuring that there is uniformity when it comes to communication between project teams and a smaller probability of making measurement errors..
Mathematical Representation and Calculations
Calculation of dimensions should be accurate and with regard to units. The formula of calculation is: Volume = (Length) (Width) (Height), while all the dimensions are given in the same system of measurement. Any cubic measurements should have all the dimensions in meters of cubic meter, feet of cubic foot or inches of cubic inch.
Two dimensions are sufficient to calculate an area of a surface: areas of rectangular surfaces are calculated as: Area = Length x Width. With non-regular shapes more elaborated formulas might be used, however, the basic rules apply. Three-dimensional objects need more area calculations in determination of surface area, which are combined in relation to geometric characteristics of the object.
Unit conversions between different types of measurements are generally needed in professional use. To perform the conversion between imperial to metric systems we should pay attention to the conversion factors 1 inch = 2.54 centimeters, 1 foot = 0.3048 meters and 1 meter = 3.28084 feet. Correct conversions of a fixed object are necessary to international projects and cross-industry cooperation.
Practical Applications Across Industries vertical dimension
Construction and Architecture
These dimensions greatly help construction professionals in ordering materials and calculating a structure and project planning. In mathematics, precise measurements typically guarantee fitting, good structure and adherence to the code. The length measurements are used to define the lumber needs in terms length, width measurement influences the design of the foundation, and height measurement defines the need of structural support, for example.
The design intent in architectural drawings is most often depicted through the inclusion of dimensional information, in sufficient detail to convey the intent in a manner that can be understood by those who use the architectural drawing. In floor plans, elevations and sections rely on proper dimensional presentation on the page . Dimensional accuracy and geometry are essential under building codes which prescribe minimum dimensions of different spaces such as the size of the room, the width of the corridor, and the height of the ceiling, which will warrant approval of permits and occupancy certificate, emphasizing the difference .
Dimensional specification is very critical in project estimation and cost. In terms of length, standard dimensional characteristics give rise to the material quantities, labor requirements, equipment needs, and the overall shape of the project adjectives long. Failure to accurately measure the quantities of materials needed in a project will cause shortages, cost overruns and delays in the completion of the project hence dimensional exactness is required to successfully complete a project.
Manufacturing and Product Design
The dimensional specifications that are needed during manufacturing processes are very strict, because the quality of products, match, and functionality depends on it. Tolerancing sets limits on the dimension variation and the tighter the tolerance, the higher the cost of the manufacturing process is, but the better the products are.
The procedures that are used in quality control are based on dimensional checks to provide specifications to the products. Other precision instrumentation, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), checks dimensional accuracy as a production process. Statistical process control refers to the values of dimensions as measurements that monitor mechanisms of stability in a given process and indicate possible occurrence of quality in a given process before it escalates into a major problem.
The packaging of the products should be dimensional and should offer protection and efficiency. The dimensions of packages should be able to fit the product dimensions and at the same time waste less materials and the cost of shipment. The dimensional optimization will have a high potential to lower packages costs, environmental influence and still be able to protect and correctly present the products.
Logistics and Shipping
Dimensional measurements are employed by shipping industries to compute volumetric weight, utilisation of containers and determine how to maximize the transportation costs. A dimensional weight calculation takes into consideration the actual weight with the calculated weight on the basis of the dimensions, and the cost of shipping is dictated by the bigger of the two values.
Dimensional data is used by warehouse management systems to plan inventory optimisation, storage efficiency and ordering fulfilment efficiency. The purpose of slotting optimization is on the basis of dimensional data so that products are placed in the correct storage areas with the least handling of products and the optimal use of spaces.
The international shipping involves dimensional compliance with several regulations and restrictions. In other words, container loading optimization employs dimensions data in trying to optimize space utilization but keeping weight distribution and cargo security intact. Oversized cargoes, such as those the size of a swimming pool, might be subjected to dimensional restrictions, which necessitate specific treatments and more documentations.
Measurement Techniques and Tools
Traditional Measurement Tools
The most popular dimensional measurement tool is the tape measure, which measures the shorter side, is portable, accurate, and easy to use in majority of applications. Professional level tape measures have stronger casings, easy lines to follow and even locking system to ensure accuracy in the measurements. In proper technique, the tape has to be straight, flat and should have appropriate tension to ensure correct readings.
Straightedges and rulers are used to give accuracy to small scale measurements and laying out. Steel rulers provide durability and precision in word length use in the workshop and can be used on curved surfaces and irregular shapes using flexible rulers. Scales that are used by the architect consist of proportional scales of scaled drawings and plans.
Calipers have accuracy in dimensions by small measures, dial in calipers are easy to read and digital calipers which are suited to electronic display and retention of data. Verner calipers are accurate and can be used on precision applications and on the other hand, the inside and outside calipers have suites to fit in innumerable situations that a caliper can be used.
Modern Digital Measurement Technology
The laser measuring equipment transforms dimensional measurement because it ensures precise measurements regardless of the presence of movements. These devices will eradicate measurement errors caused by spine areas in the tapes and will enhance safety because it will not require one to access the points of measurement physically to get measurements. A lot of laser measurements have the area and volume computing features.
Digital measuring systems combine several technologies of measurement to make an in-depth dimensional analysis. Photogrammetry involves the digital camera to produce accurate measurements of the images, and 3D scanning technology provides dimensional models of complicated objects and spaces.
There has also been an increase in mobile applications, where the smart phone cameras and sensors may be used as measurement devices. These tools are not accurate enough to be used with precision but are convenient when making preliminary measurements and even just a quick look up. Augmented reality programs superimpose dimensional data on the real-life pictures to improve visual displays.
Conclusion
Knowledge of width, length, height, and depth is the basis of any dimensional analysis in every industry. The four basic measurements will give the physical data needed in designing, construction, making and logistics activities. Measurement techniques, notation conventions, and practical applications are the measures that need to be mastered in regard to being a competent professional, which can be summarized in a table for clarity.
The measures that should be taken in order to be effective in the use and measurement of dimensional measurement include, choosing the correct tools, adhering to industry practice, and ensuring uniformity. Working either with old-fashioned measuring devices or digital technology, these principles will always be the same: being a professional depends on the precision, accuracy and the focus on the details.
